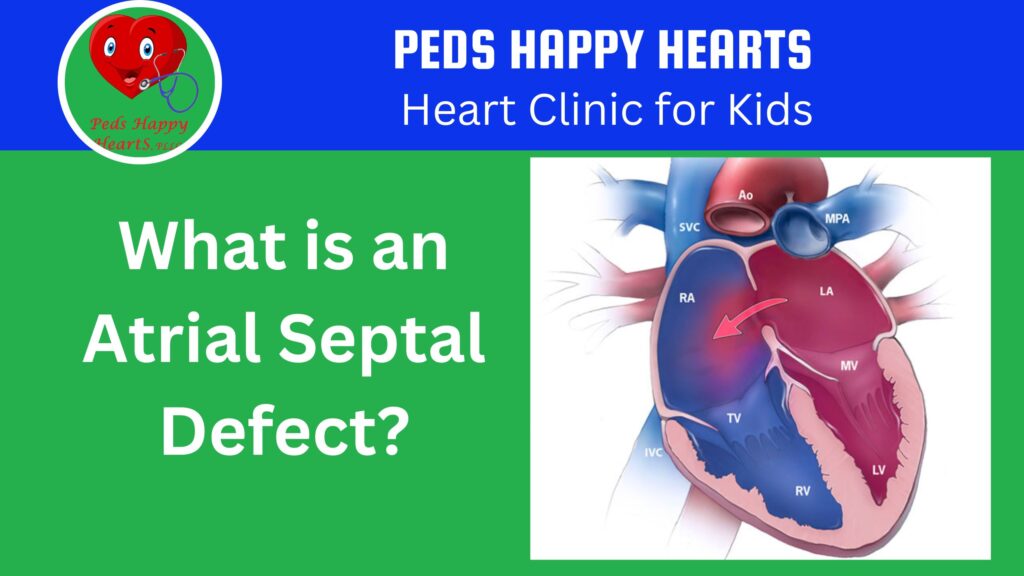
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect that affects the structure of the heart. It occurs when there is a hole in the wall (septum) between the two upper chambers of the heart (atria). This hole allows oxygen-rich blood to flow from the left atrium into the right atrium, which then mixes with oxygen-poor blood and is pumped to the lungs.
ASD can vary in size and location, and in some cases, it may close on its own as the child grows. However, larger defects may require treatment to prevent complications such as heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and stroke.
Symptoms of Atrial Septal Defect:
Symptoms of ASD may not be noticeable in some cases, and the defect may be detected during routine check-ups or tests for other conditions. However, some people may experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs, feet or abdomen, and heart palpitations.
How to Diagnose ASD:
Diagnosis of ASD involves physical exams, electrocardiogram (ECG), chest X-rays, and echocardiogram.
Physical Exam: A heart murmur may be appreciated due to relative pulmonary stenosis (more blood flow to the lungs). Fixed S1 and S2 heard sound due to pulmonary hypertension. However, most patients do not have a heart murmur.
Chest X-Ray: There may be cardiomegaly (heart enlargement) from the right sided heart being enlarged.
Electrocardiogram: There are signs the right heart is enlarged (peaked p waves, right ventricular enlargement, or right axis deviation).
Echocardiogram: Heart ultrasound that will show a hole in the heart’s upper chamber. It may need a bubble study if it is not obvious.
Treatment:
Treatment options may include medication to manage symptoms, surgery to repair the defect, or closure of the defect using a device inserted through a catheter via a cardiac catheterization procedure.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you or your child may have ASD. Waiting too long can lead to pulmonary hypertension in adults, which can be irreversible. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes.
To schedule a cardiac evaluation, contact our office at 406-272-2376.